How To Read This Report
The NDC x SDG approach focuses on identifying the key interlinkages and pathways through which priority climate actions can accelerate a country’s most vital development goals. In doing so, it helps craft a clear, evidence-based narrative that brings together broad coalitions across government to drive coordinated progress.
The report is divided into four categories of analysis →
- NDC x SDG Moment — human progress within planetary boundaries is the next development frontier. This section provides a snapshot of key climate and human development data.
- NDC x SDG Alignment — maps climate commitments and national development priorities using custom machine learning tool that draws from an SDG vocabulary of 100k terms.
- NDC x SDG Interlinkages — identifies national-level actions through enhanced NDCs that accelerate SDG achievement and advances a robust development case.
- Finance & Stimulus — charts fiscal constraints and stimulus opportunities to ensure climate and development policy choices can be advanced with greatest impact.
1. NDC x SDG Moment
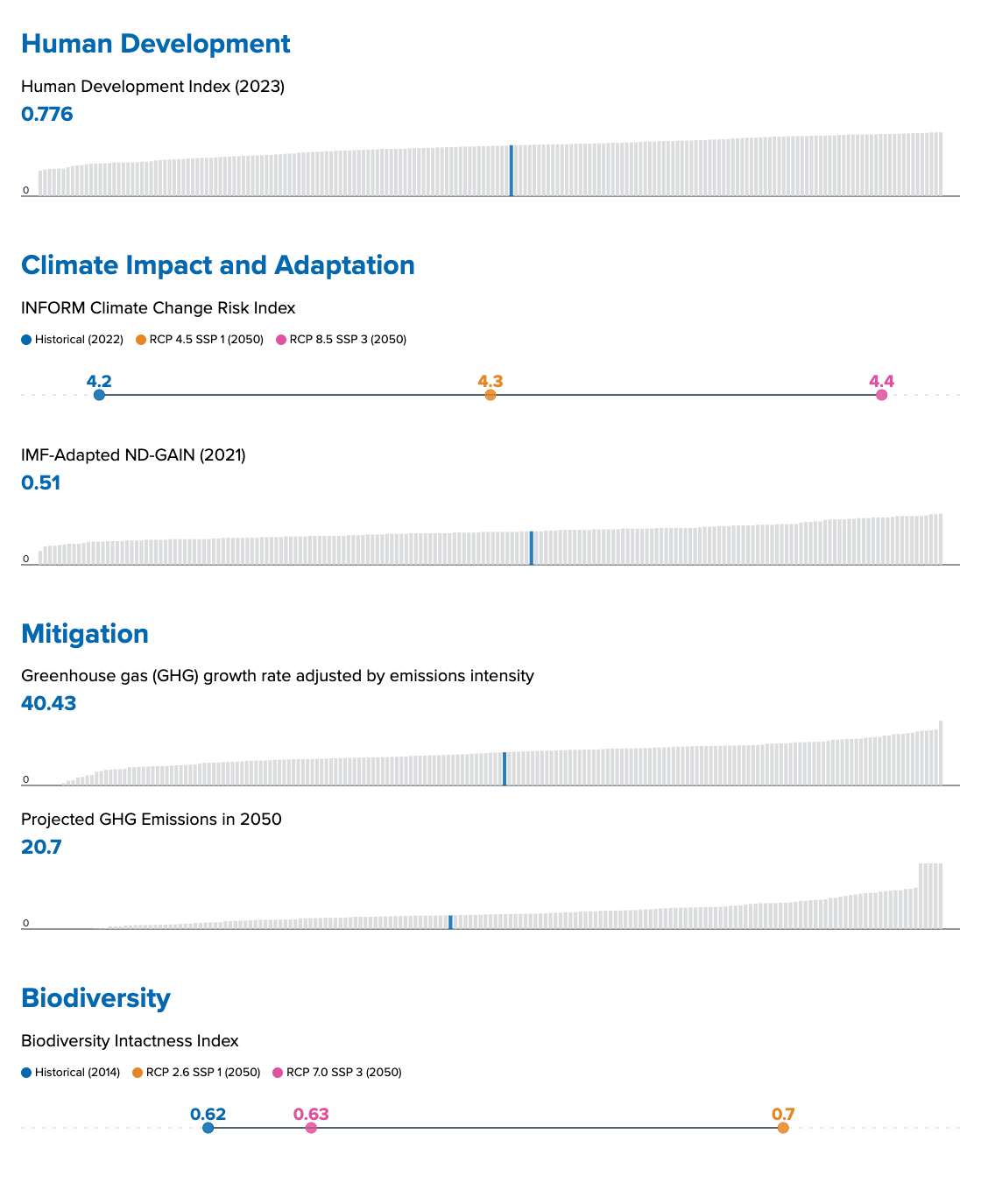
This section takes stock of the country’s current climate and sustainable development context, providing a clear snapshot of key climate and human development data and setting the scene to identify climate–development synergies.
As part of their NDC the Dominican Republic has set a target of reducing emissions by
13.85 MtCO2e
(27%)
Sources European Commission 2023 (INFORM Climate Change Risk Index), IMF 2022 (IMF-Adapted ND-GAIN Index); Environmental Performance Index 2024 (GHG growth rate adjusted by emissions intensity & Projected Emissions in 2050); Helen Phillips; Adriana De Palma; Ricardo E Gonzalez; Sara Contu et al. 2021 (Biodiversity Intactness Index).
NDC x SDG Alignment
Goal Level
This analysis shows the most prominent SDGs in each of the two national strategies on climate and development. This identifies areas of common action and potential synergies across national climate and development priorities.
Nationally Determined Contributon (NDC)
Note: Based on Updated Nationally Determined Contribution (2020)
National Development Plan(s) (NDP)
Note: Based on Pluriannual National Plan of the Public Sector
These visuals are generated by analyzing the NDCs and National Development Plans through the SDG framework at goal level.
NDC x SDG Alignment
Target Level
This analysis shows how the country’s climate actions, both mitigation and adaptation, align with and drive impact across the SDGs at the target level.
Mitigation NDCs
Adaptation NDCs
These visuals are generated by analyzing NDC actions through a custom-built AI tool and categorized using the SCAN tool to surface relevant SDG synergies at the Goal level. For additional information on the NDC-SDG mapping, please visit: https://ambitiontoaction.net/scan_tool/
NDC x SDG Alignment
Action Level
This section breaks down the NDC categories into specific country commitments identified through a custom-built AI tool. The bubble sizes show how many actions fall under each category, helping pinpoint where NDC–SDG acceleration is most likely.
Dominican Republic 's NDC includes actions in these sectors:
Mitigation
Adaptation
3. NDC x SDG Interlinkages
NDC x SDG interlinkages reveal how climate actions can impact human development progress. Building from the country's NDC actions and SDG priorities, the following integrated SDG pathways reflect NDC actions with the most potential to accelerate the SDGs.
4. Finance & Stimulus
This section examines a country's fiscal space and public investment priorities, highlighting opportunities to align stimulus measures with SDG progress and accelerated climate action.
Many countries are facing reduced fiscal space, high debt levels, rising interest rates and downgrades on credit ratings. Fiscal and financial constraints tend to slow or even reverse SDG progress.
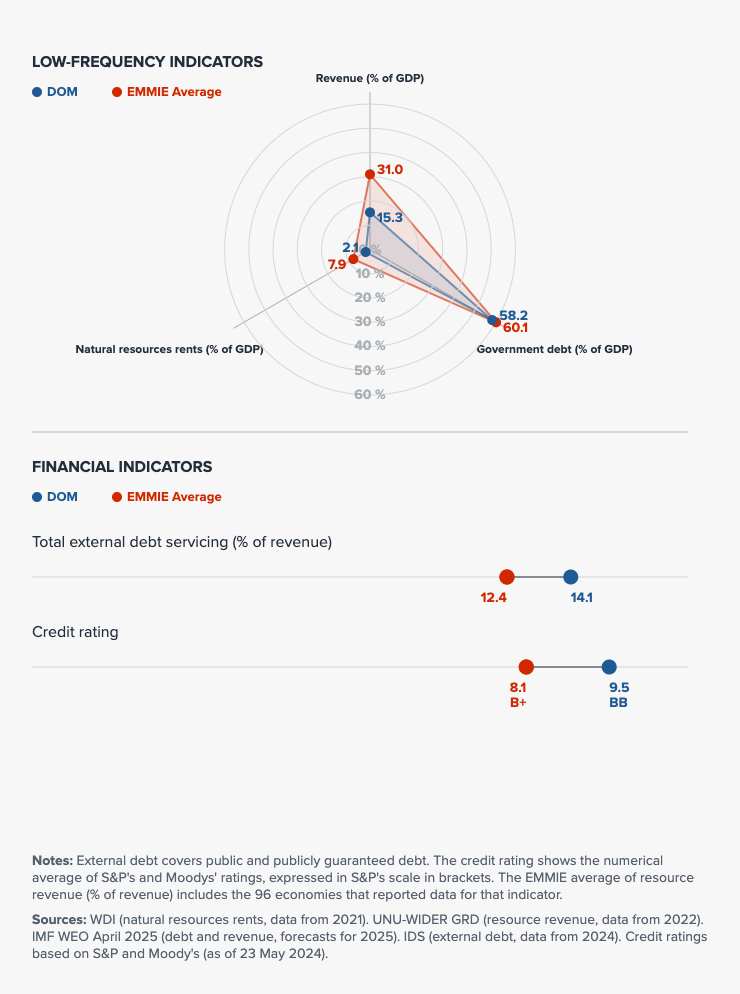
Public Finance
Financing needs
SDGs: Over 6,900 million USD per annum in capital investment required for achieving SDGs (IMF)
NDC: Total: Estimated 20.45 billion USD total by 2030
- 10.34 billion USD for mitigation
- 10.11 billion USD for adaptation
Financing strategy
The Dominican Republic is advancing in mobilizing financial resources to meet its climate and sustainable development commitments. Since 2021, it has been reviewing its planning and budget management to strengthen investment decisions, monitoring, and spending efficiency. The country is designing a National Climate Finance Strategy that promotes green financing instruments, long-term public-private cooperation, and enhanced engagement with the Green Climate Fund, with estimated investments exceeding USD 20.45 billion in mitigation and adaptation for 2021–2030.
Expenditures & budgets
The Dominican Republic’s public budgeting system aligns with the SDGs through its linkage to the National Planning and Public Investment System. The 2024–2027 Multiannual Budget Framework prioritizes key sectors like health, education, environment, and social protection, assigning and protecting budgets annually. However, SDG alignment could improve through systematic budget tagging and stronger programmatic integration.
Debt instruments
The Dominican Republic issued its first sovereign green bond on June 25, 2024, in the international market for USD 750 million, with a 12-year maturity and a coupon of approximately 6.6 percent. It also adopted a Green, Social, and Sustainability Bond Framework in June 2024, defining eligible sectors such as clean transport, renewable energy, waste management, water, health, and education.
International climate finance
The Dominican Republic has received international climate finance from the Green Climate Fund through projects such as FP174 with USD 174.3 million, FP242, and FP237; the Adaptation Fund with approximately USD 10 million; and the Global Environment Facility with USD 12.6 million in grants via the Small Grants Programme. It also benefits from Euroclima technical assistance and an endorsed USD 85 million Climate Investment Funds plan.
Private Finance & Economy
Policy & Regulatory Measures:
Innovative Instruments:
A total of thirteen innovative financial instruments were identified and assessed to support the financing of the National Development Strategy and the prioritized Sustainable Development Goals. Among them are thematic bonds, including green, social, sustainable, and sustainability-linked bonds, debt-for-nature swaps, diaspora financing through various forms of remittances and equity participation, payments for environmental services, Public-Private Partnerships for sustainable development, carbon credits, and carbon taxes
International Investment:
Recent international investments in the Dominican Republic include a USD 750 million sovereign green bond for clean transport and renewables, a USD 174 million GCF adaptation program, World Bank-backed climate reforms, IDB-financed water projects, and TotalEnergies’ renewable and LNG ventures supporting the country’s energy transition.
Domestic Investment:
Private investment in the Dominican Republic averaged around 25% of GDP in recent years, supported by robust growth in construction, tourism, and FDI, though tight monetary policy in 2023 moderated expansion.
SDG Investor Map
17 Investment Opportunity Areas (IOAs) that contribute to the government’s NDC priorities and meet SDG needs. The priority IOAs span 8 climate-relevant sectors in Dominican Republic:
Development Breakthrough
Policy Brief
Each NDC x SDG Insights policy brief is a focused, country-specific deep dive that builds on the broader Insights report to unpack a single development breakthrough, outlining its policy implications and the SDG-positive actions driving it forward.